Have you ever dreamed of growing fresh, organic vegetables and raising fish at the same time? With an **aquaponics system**, you can do just that Combining the best of hydroponics (growing plants without soil) and aquaculture (raising fish), aquaponics offers a sustainable and efficient way to grow food right at home. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the **steps to build and maintain a home aquaponics system**, so you can enjoy a self-sustaining garden year-round.

### What is Aquaponics?
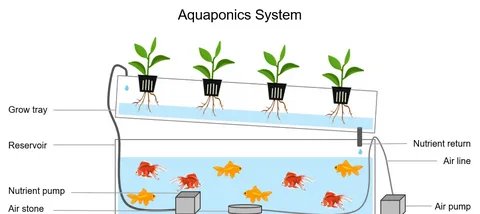
Aquaponics is a method of growing plants and raising fish in a symbiotic environment. Fish produce waste that provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants help filter and clean the water, which is then returned to the fish tanks. This closed-loop system makes aquaponics incredibly efficient, requiring less water than traditional soil gardening and no chemical fertilizers.
### Why Choose Aquaponics?

– **Sustainable**: Aquaponics is eco-friendly and water-efficient. It uses up to **90% less water** compared to traditional farming.
– **Space-Saving**: It’s perfect for small spaces, such as apartments, urban gardens, or homes with limited yard space.
– **Fresh Produce and Fish**: You can harvest both **fresh vegetables** and **healthy fish** without relying on external food sources.
– **Low Maintenance**: Once set up, aquaponics systems are relatively low-maintenance and can thrive with minimal intervention.
### Building Your Home Aquaponics System
Before you start, you’ll need to gather a few materials. Here’s a basic list of the **components** needed for a simple home aquaponics system:
#### Materials:

– **Fish Tank**: This is where your fish will live. The size will depend on how many fish you plan to raise and how large your system will be.
– **Grow Bed**: This is where your plants will grow. It can be made from plastic or wood and should be large enough to support your plant-growing needs.
– **Water Pump**: A water pump circulates the water between the fish tank and the grow bed, ensuring that nutrients are constantly supplied to the plants.
– **Grow Media**: Materials like **expanded clay pellets**, **gravel**, or **lava rocks** provide support for plant roots and allow for proper drainage.
– **PVC Pipes or Tubing**: Used to transport water between the tank and the grow bed.
– **Aerator**: Helps to oxygenate the water, which is essential for both the fish and the plants.
– **Fish**: Tilapia, goldfish, or koi are popular choices for home aquaponics systems.
#### Step 1: Choose the Right Location
Pick a **location** that receives plenty of natural sunlight (6-8 hours a day) for your plants. It’s also important to place your system in a space with good ventilation to ensure a healthy environment for both your fish and plants. If you live in a colder climate, consider placing the system indoors or setting up a **greenhouse**.
#### Step 2: Set Up the Fish Tank
– **Install the Fish Tank**: Choose a tank size based on how many fish you plan to raise. A good starting point is to have at least **1 gallon of water** per inch of fish.
– **Fill with Water**: Fill the tank with water and allow it to stabilize for a few days before introducing fish. You can use a water conditioner to remove chlorine and ensure the water is safe for fish.
#### Step 3: Set Up the Grow Bed
– **Install the Grow Bed**: Your grow bed should sit above the fish tank, allowing water to flow from the tank to the bed and return easily. **Flood-and-drain systems** (also called **media-filled beds**) are ideal for home systems. These beds are filled with a grow medium like clay pebbles, which supports the plants and provides aeration to the roots.
– **Position the Grow Bed**: Place the grow bed on top of the fish tank or near it, with pipes or tubing that will carry water from the tank to the bed.
#### Step 4: Connect the Plumbing
– **Install PVC Pipes**: Connect the water pump to the fish tank using PVC pipes or flexible tubing. The pump will push water up to the grow bed. The water should then flow back to the fish tank through a return pipe.
– **Check for Leaks**: Test the water flow to ensure there are no leaks and that the system is circulating properly.
#### Step 5: Add Fish to the Tank
– **Choose Your Fish**: Start with hardy fish species like **tilapia**, **trout**, or **goldfish**. It’s important to select fish that thrive in your local climate.
– **Introduce the Fish Gradually**: Begin with a small number of fish, as adding too many at once can overwhelm the system. Over time, as the system matures, you can gradually add more fish.
#### Step 6: Add Plants to the Grow Bed
– **Select Plants**: Aquaponics systems work well for **leafy greens** like lettuce, spinach, and kale, as well as herbs such as basil, mint, and parsley. Fruit-bearing plants like tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries can also thrive in larger systems.
– **Plant in the Grow Bed**: Gently place the plants into the grow medium, ensuring the roots are well-supported. Water them lightly until the system is fully functional.
### Maintaining Your Aquaponics System
While aquaponics systems are relatively low-maintenance, they still require attention to keep everything in balance. Here’s how to ensure your system stays healthy:
#### 1. Monitor Water Quality
– **Test Water pH**: The ideal pH for an aquaponics system is between **6.8-7.0**. If the pH is too high or too low, it can affect the health of both the fish and plants. You can adjust the pH using natural remedies, such as adding **vinegar** to lower the pH or **lime** to raise it.
– **Check Ammonia and Nitrites**: Fish produce waste that breaks down into ammonia. You need to ensure that the **nitrification process** is working, as ammonia is toxic to fish. Regularly test the water for ammonia and nitrite levels and make adjustments if needed.
#### 2. Feed the Fish
– **Feed your Fish**: Fish should be fed a balanced diet that matches their species. Overfeeding can lead to excess waste in the water, so feed only what the fish can consume in 5-10 minutes.
– **Observe Fish Behavior**: Healthy fish will swim actively and feed regularly. If they seem sluggish or stop eating, this could be a sign of water quality problems.
#### 3. Prune and Harvest Plants
– **Prune Regularly**: Prune your plants regularly to encourage healthy growth and prevent overcrowding. Remove dead leaves and stems to avoid clogging the system.
– **Harvest Your Crops**: As your plants mature, you can start harvesting. Harvesting regularly helps the plants continue to grow and keeps the system in balance.
#### 4. Maintain the Pump and Filtration System
– **Clean the Pump**: Periodically clean the water pump to ensure it’s functioning properly. Build-up can clog the system, affecting water circulation.
– **Check the Filtration System**: If your system includes a filtration component, clean or replace the filters regularly.
Building and maintaining an **aquaponics system** at home is a rewarding way to grow fresh, organic food while raising fish in a sustainable environment. With the right setup, you can enjoy a thriving system that produces both healthy fish and delicious vegetables. While it requires some initial investment of time and effort, the rewards are well worth it—fresh, homegrown food all year long
Start small, and with proper care and attention, you’ll have your own self-sustaining, eco-friendly aquaponics system running smoothly in no time 🐟🌱
