Grafting is one of the most effective techniques for propagating fruit trees, **allowing gardeners and orchardists to combine the best characteristics of different trees into one thriving plant**. By mastering this technique, you can produce **disease-resistant, high-yielding, and better-tasting fruit trees** while also saving money and time.
This step-by-step guide will walk you through **the essential tips for successful grafting**, ensuring strong, healthy tree growth and abundant fruit production. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, these methods will help you achieve the best results.
## **What is Grafting and Why is it Important?**
Grafting is a **horticultural technique** that involves joining two different plants to create a single, stronger tree. It consists of:
– The **rootstock** (the lower part, which provides the root system)
– The **scion** (the upper part, which determines the fruit type)
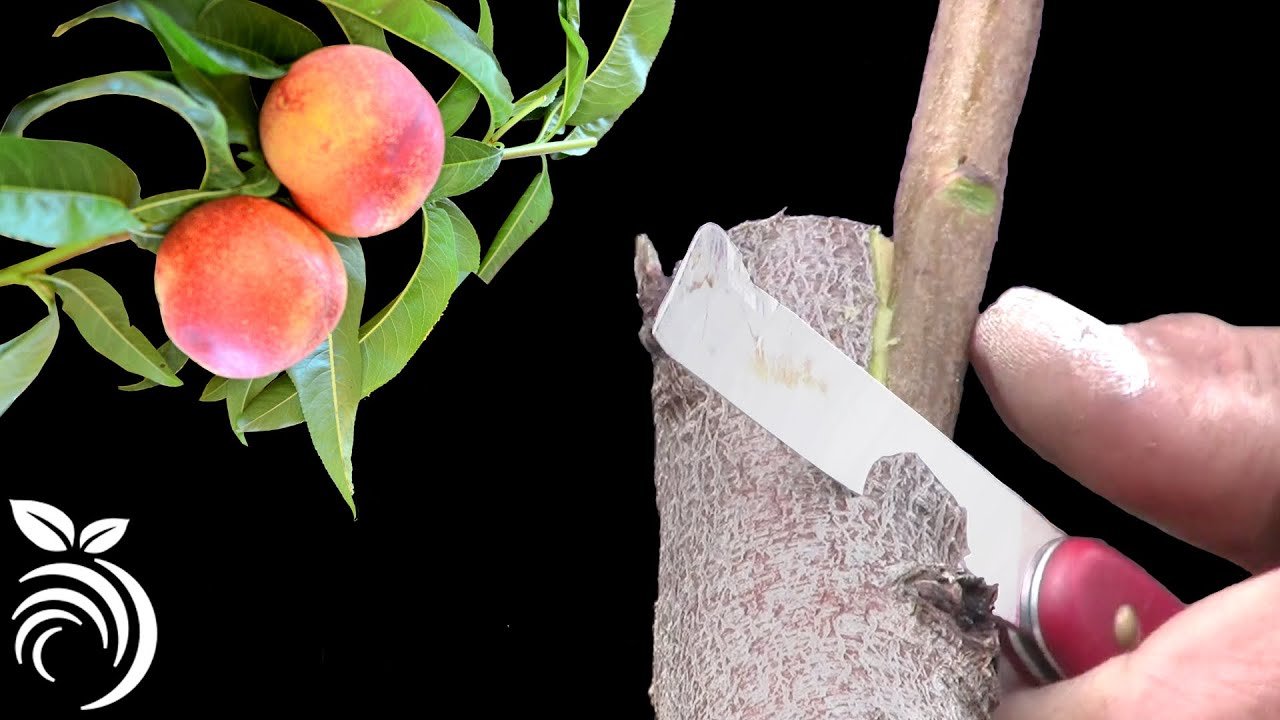

By combining these two parts, **grafting enhances fruit quality, improves disease resistance, and speeds up fruit production compared to growing from seeds**. It is widely used for apples, pears, citrus, and stone fruits like peaches and cherries.
## **Tools and Materials You Need for Grafting**
Before starting, make sure you have the right tools:
✅ **Sharp grafting knife** – Ensures clean, precise cuts
✅ **Pruning shears** – For trimming branches
✅ **Grafting tape or rubber bands** – Secures the graft in place
✅ **Wax or grafting sealant** – Prevents drying and infections
✅ **Alcohol or bleach solution** – Sterilizes tools to prevent disease transfer
✅ **Healthy rootstock and scion wood** – The key to successful grafting
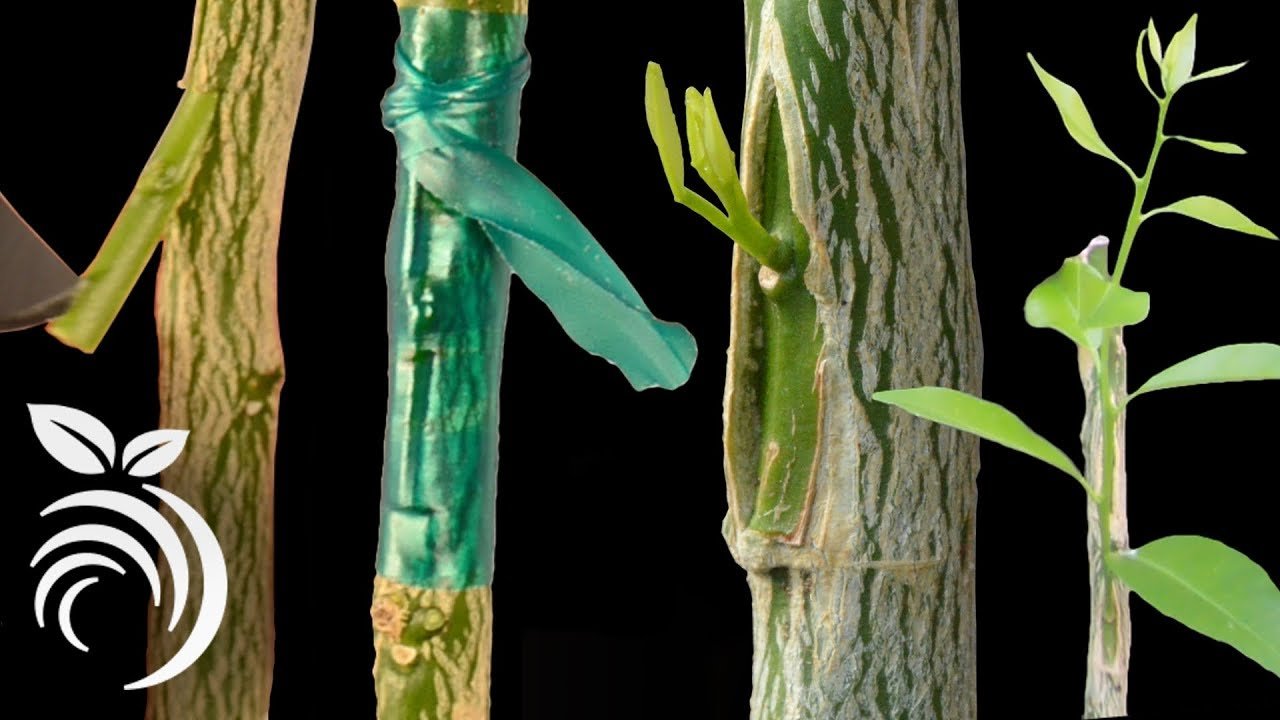

## **Choosing the Right Rootstock and Scion**
– **Rootstock Selection:** Choose a rootstock that is **disease-resistant, hardy, and well-adapted to your climate**. Dwarfing rootstocks help control tree size and increase fruit production.
– **Scion Selection:** Pick a scion from a **healthy, high-yielding tree with desirable fruit traits**. Ensure it has at least 2-3 buds and is collected during dormancy (late winter or early spring).
## **Best Grafting Methods for Fruit Trees**
Different grafting techniques work best for different tree types and sizes. Here are some of the most effective methods:
### **1. Whip and Tongue Grafting (Best for Young Trees)**
– Used for fruit trees like apples and pears.
– Creates a strong union by interlocking the cuts of the rootstock and scion.
### **How to Do It:**
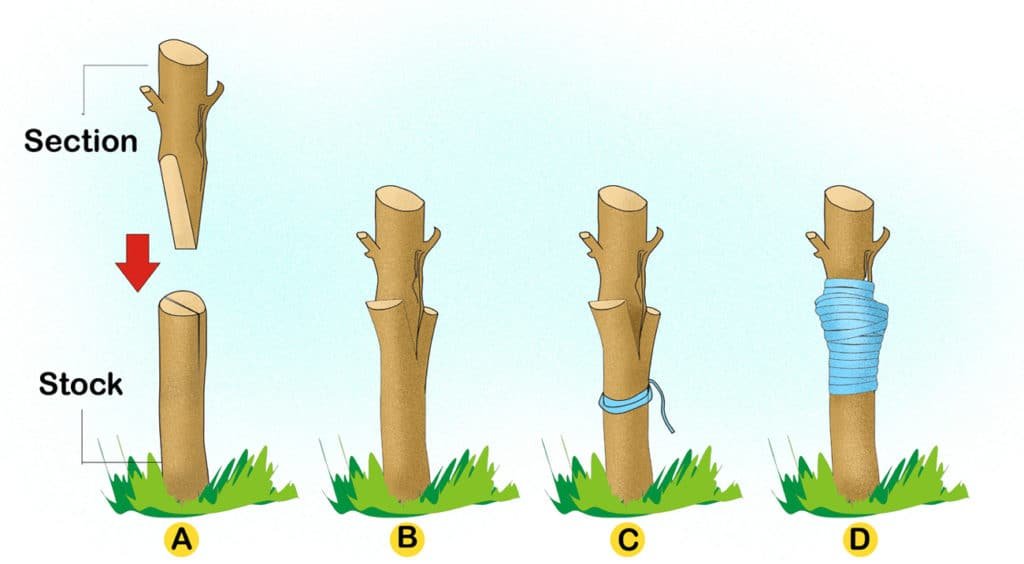
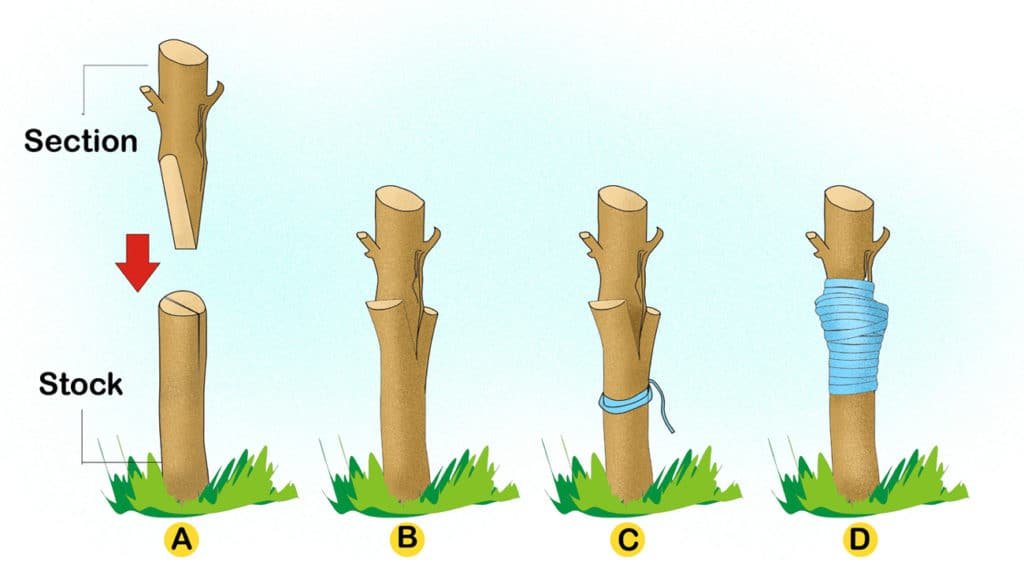
### **2. Cleft Grafting (Best for Large Rootstocks or Older Trees)**
– Ideal for top-working an existing tree to change its fruit variety.
### **How to Do It:**
1. Make a vertical cut (2 inches deep) in the center of the rootstock.
2. Prepare two scions with wedge-shaped ends.
3. Insert the scions into the cut, ensuring the cambium layers align.
4. Wrap with tape and seal with wax.
### **3. Bud Grafting (Best for Citrus and Stone Fruits)**
– Uses a single bud instead of a full scion.
### **How to Do It:**
1. Cut a small bud from a healthy scion.
2. Make a T-shaped incision in the rootstock.
3. Insert the bud under the bark.
4. Wrap with grafting tape and wait for the bud to grow.
## **Best Time to Graft Fruit Trees**
Timing is crucial for grafting success. The best period depends on the type of graft:
– **Spring (Late Winter to Early Spring)** – Ideal for most grafting techniques when trees are still dormant.
– **Summer (Mid to Late Summer)** – Best for bud grafting when sap flow is strong.
## **Essential Tips for Grafting Success**
✔ **Choose compatible trees** – Some fruit trees graft well together (e.g., apple on apple, pear on pear). Avoid incompatible pairings.
✔ **Match the cambium layers** – The cambium (green growing layer under the bark) of the scion and rootstock **must align** for successful grafting.
✔ **Keep scions fresh** – Store in a damp paper towel inside a plastic bag in the fridge until ready to use.
✔ **Seal the graft properly** – Prevent moisture loss by wrapping with grafting tape and applying wax or sealant.
✔ **Protect from extreme weather** – Provide shade or shelter if the tree is exposed to excessive sun, wind, or frost.
✔ **Be patient** – Some grafts take weeks or even months to fully heal and start growing.
## **Caring for Newly Grafted Trees**
After grafting, proper care ensures strong healing and successful growth:
– **Monitor moisture levels** – Water regularly but avoid overwatering.
– **Check for new growth** – If the scion starts sprouting leaves, the graft has taken successfully.
– **Remove competing shoots** – Prune any shoots that grow below the graft to direct energy to the scion.
– **Loosen grafting tape over time** – As the tree heals, make sure the tape does not constrict growth.
## **Benefits of Grafting Your Own Fruit Trees**
✅ **Grow multiple fruit varieties on one tree** – Perfect for small gardens
✅ **Faster fruit production** – Grafted trees produce fruit **years earlier than seed-grown trees**
✅ **Disease-resistant trees** – Select strong rootstocks for healthier growth
✅ **Cost-effective** – No need to buy new trees when you can graft your own
## **Final Thoughts: Master Grafting and Grow Your Best Fruit Trees**
Grafting is an **invaluable skill** for any fruit tree grower. By following these essential tips and step-by-step methods, you can successfully graft fruit trees **for stronger growth, higher yields, and better-quality fruit**.
Whether you’re creating a **multi-fruit tree**, reviving an old tree, or developing your own unique hybrid, grafting opens up **endless possibilities** for your garden.
Start grafting today and enjoy the benefits of **healthy, productive fruit trees for years to come**