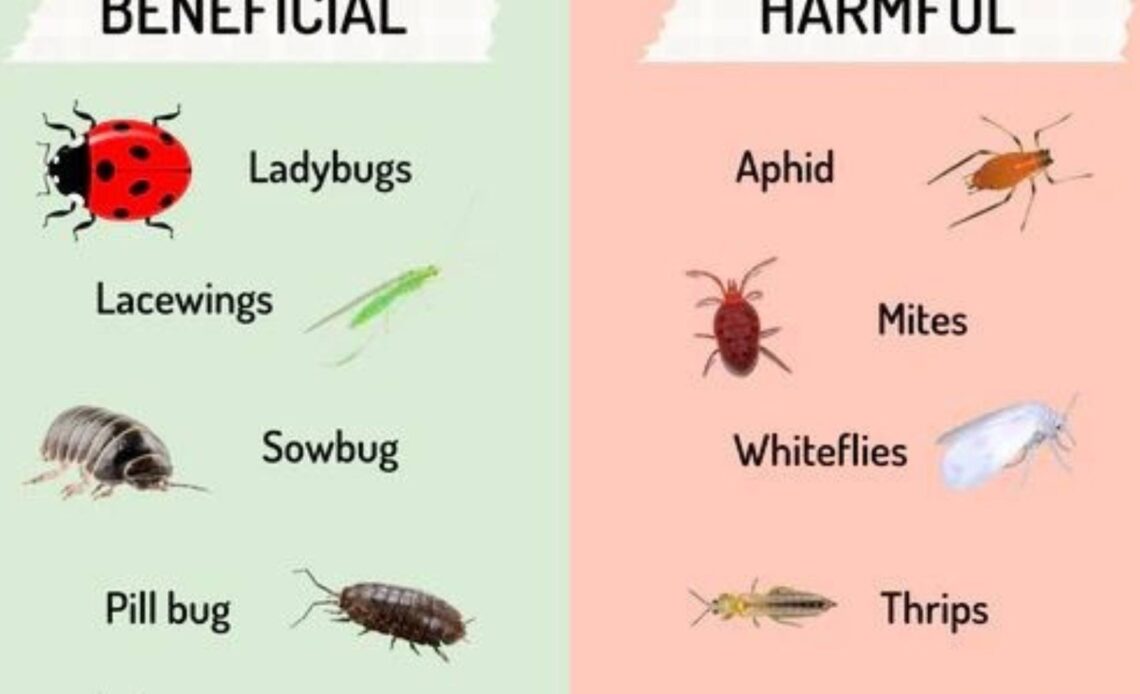
Insects are a crucial part of any garden ecosystem. Some insects serve as protectors, keeping harmful pests under control, while others cause significant damage to plants, leading to poor growth and reduced yields. Understanding the difference between beneficial and harmful insects is essential for effective pest management and a thriving garden.
This guide will help you identify garden-friendly insects, recognize destructive pests, and implement natural control methods to maintain a balanced ecosystem.
## **The Role of Insects in Your Garden**
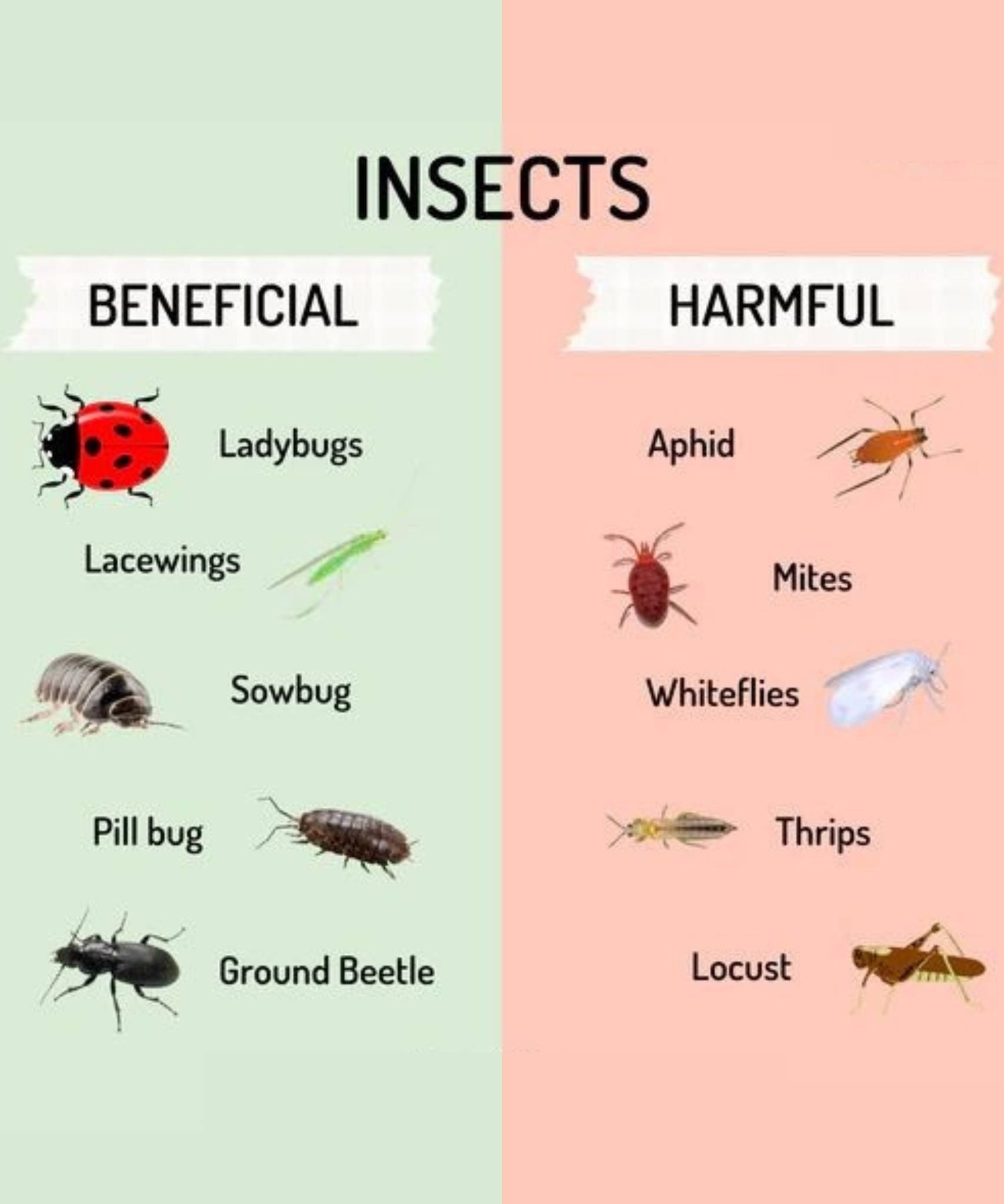
Insects play a dual role in gardening. Some species help by pollinating flowers, breaking down organic matter, and preying on harmful pests. Others, however, feed on plant sap, chew leaves, and spread diseases, making pest control a necessary part of gardening.
By identifying which insects benefit or harm your plants, you can take informed actions to promote a healthy garden without excessive use of chemical pesticides.
## **Beneficial Insects: Nature’s Pest Control**
Beneficial insects act as natural predators, pollinators, or decomposers that support plant growth. Encouraging these insects in your garden can reduce the need for chemical pesticides and help maintain a balanced ecosystem.
### **Predatory Insects That Control Pests**

These insects actively hunt and consume harmful pests, keeping their populations in check.
1. **Ladybugs (Lady Beetles)** – Ladybugs are one of the most well-known beneficial insects. They feed on aphids, mites, scale insects, and whiteflies, making them valuable allies for controlling plant-damaging pests.
2. **Lacewings** – Lacewing larvae, often called “aphid lions,” devour aphids, thrips, mealybugs, and caterpillar eggs. Adult lacewings are also pollinators.
3. **Ground Beetles** – These nocturnal hunters feed on slugs, caterpillars, and root maggots, helping protect vegetable crops.
4. **Praying Mantises** – Praying mantises eat a wide range of insects, including grasshoppers, moths, and beetles. However, they are indiscriminate predators and may also consume beneficial insects.
5. **Hoverflies** – While adult hoverflies assist in pollination, their larvae are efficient predators that consume aphids, mealybugs, and soft-bodied pests.
### **Pollinators That Boost Plant Growth**
Pollinators play a vital role in plant reproduction by transferring pollen between flowers, leading to fruit and seed development.
1. **Bees** – Essential pollinators, bees increase crop yields and support biodiversity. Planting nectar-rich flowers attracts bees to the garden.
2. **Butterflies** – These insects help pollinate a variety of flowers while adding beauty to the landscape.
3. **Moths** – Some moth species, such as hawk moths, pollinate flowers that bloom at night.
### **Decomposers That Improve Soil Health**
Decomposing insects break down organic matter, enriching the soil and enhancing plant growth.
1. **Sowbugs and Pill Bugs** – These small crustaceans consume decaying plant material, contributing to soil aeration.
2. **Dung Beetles** – By breaking down animal waste, dung beetles help recycle nutrients into the soil.
Encouraging beneficial insects by planting diverse flowering plants, avoiding chemical pesticides, and providing shelter helps create a balanced ecosystem where helpful predators keep harmful pests under control.
## **Harmful Insects: Destructive Pests in the Garden**

While beneficial insects support plant growth, harmful insects damage plants by feeding on leaves, stems, roots, and sap. Identifying these pests early is key to preventing widespread infestations.
### **Sap-Sucking Insects That Weaken Plants**
Sap-sucking insects extract nutrients from plants, leading to yellowing, wilting, and stunted growth.
1. **Aphids** – These small insects cluster on new growth and leaves, weakening plants and transmitting viruses.
2. **Whiteflies** – Whiteflies feed on plant sap and secrete honeydew, which promotes mold growth.
3. **Mites** – Spider mites cause stippled leaves and webbing, damaging fruits and vegetables.
4. **Thrips** – Thrips suck plant juices and spread diseases that cause leaf distortion.
### **Leaf-Chewing Insects That Defoliate Plants**
Leaf-chewing insects create holes and ragged edges on leaves, reducing the plant’s ability to photosynthesize.
1. **Caterpillars** – Many caterpillar species, including cabbage loopers and tomato hornworms, consume large portions of leaves.
2. **Grasshoppers and Locusts** – These insects feed on leaves and stems, causing widespread damage in vegetable gardens.
3. **Beetles** – Some beetles, like the Colorado potato beetle and flea beetles, feed on plant foliage.
### **Root-Damaging Insects That Stunt Growth**
Underground pests attack roots, leading to poor nutrient uptake and weak plants.
1. **Root Maggots** – These larvae attack crops like cabbage, onions, and radishes, causing plants to wilt.
2. **Wireworms** – The larvae of click beetles, wireworms burrow into roots, damaging vegetables such as potatoes and carrots.
## **Natural Pest Control Strategies**
Instead of relying on chemical pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects and pollute the environment, try these natural pest control methods to maintain a healthy garden.
### **Attract Beneficial Insects**
1. **Plant Companion Flowers** – Flowers such as marigolds, lavender, and dill attract pollinators and predatory insects.
2. **Create Shelter** – Install insect hotels, rock piles, or small logs to provide hiding places for beneficial insects.
3. **Avoid Chemical Sprays** – Chemical pesticides kill both good and bad insects. Use organic alternatives to protect beneficial species.
### **Use Organic Pest Control Methods**
1. **Neem Oil Spray** – A natural insecticide that repels aphids, whiteflies, and mites without harming beneficial insects.
2. **Garlic or Chili Pepper Spray** – Homemade sprays deter pests while being safe for plants and helpful insects.
3. **Hand-Picking Pests** – Manually removing caterpillars, beetles, and larger insects prevents infestations.
### **Crop Rotation and Companion Planting**
1. **Rotate Crops** – Changing plant locations each season disrupts pest life cycles and reduces soil-borne diseases.
2. **Use Companion Plants** – Some plants repel pests when grown together. For example, basil deters aphids when planted near tomatoes.
### **Improve Soil Health**
1. **Add Compost and Mulch** – Healthy soil supports strong plants that can resist pests.
2. **Encourage Earthworms** – Earthworms improve soil structure and nutrient availability.
By implementing these natural pest control strategies, gardeners can create a thriving, balanced ecosystem where beneficial insects outcompete harmful pests.
## **Finding the Balance: The Key to a Healthy Garden**

The key to successful gardening lies in recognizing the balance between beneficial and harmful insects. Instead of viewing all insects as threats, consider how they interact within the ecosystem. Encouraging predators, improving plant health, and using organic pest control measures ensure that plants can flourish without excessive chemical intervention.
Next time you see an insect in your garden, ask yourself: is it a friend or a foe? By identifying the role each insect plays, you can take strategic steps to protect your plants and cultivate a thriving, pest-resistant garden.
Are you ready to embrace the hidden battle of insects in your garden? Start observing, protecting beneficial species, and using sustainable pest control methods to transform your garden into a thriving, natural paradise.