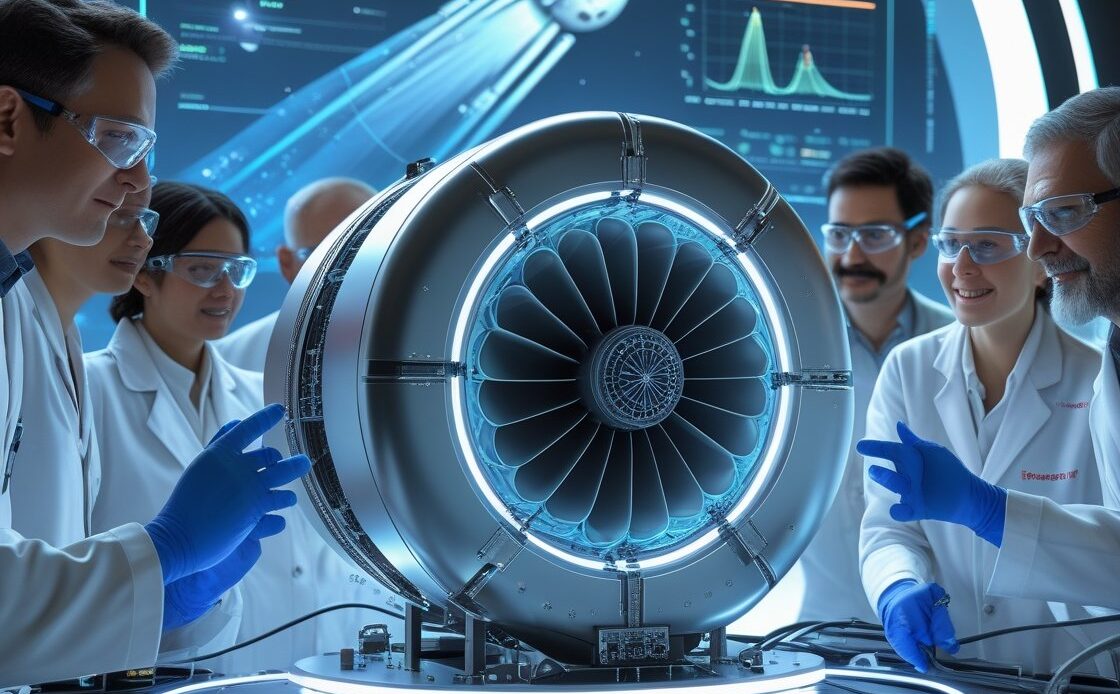
In a monumental leap forward for space exploration, Rosatom scientists have unveiled a prototype plasma rocket engine that promises to revolutionize the way we travel through space. This cutting-edge technology could drastically reduce the time it takes to reach Mars, with estimates suggesting that the journey could be completed in just 30 to 60 days—something previously thought to be a far-off dream. This breakthrough has the potential to change the course of humanity’s exploration of deep space and possibly pave the way for manned missions to the Red Planet in the near future.
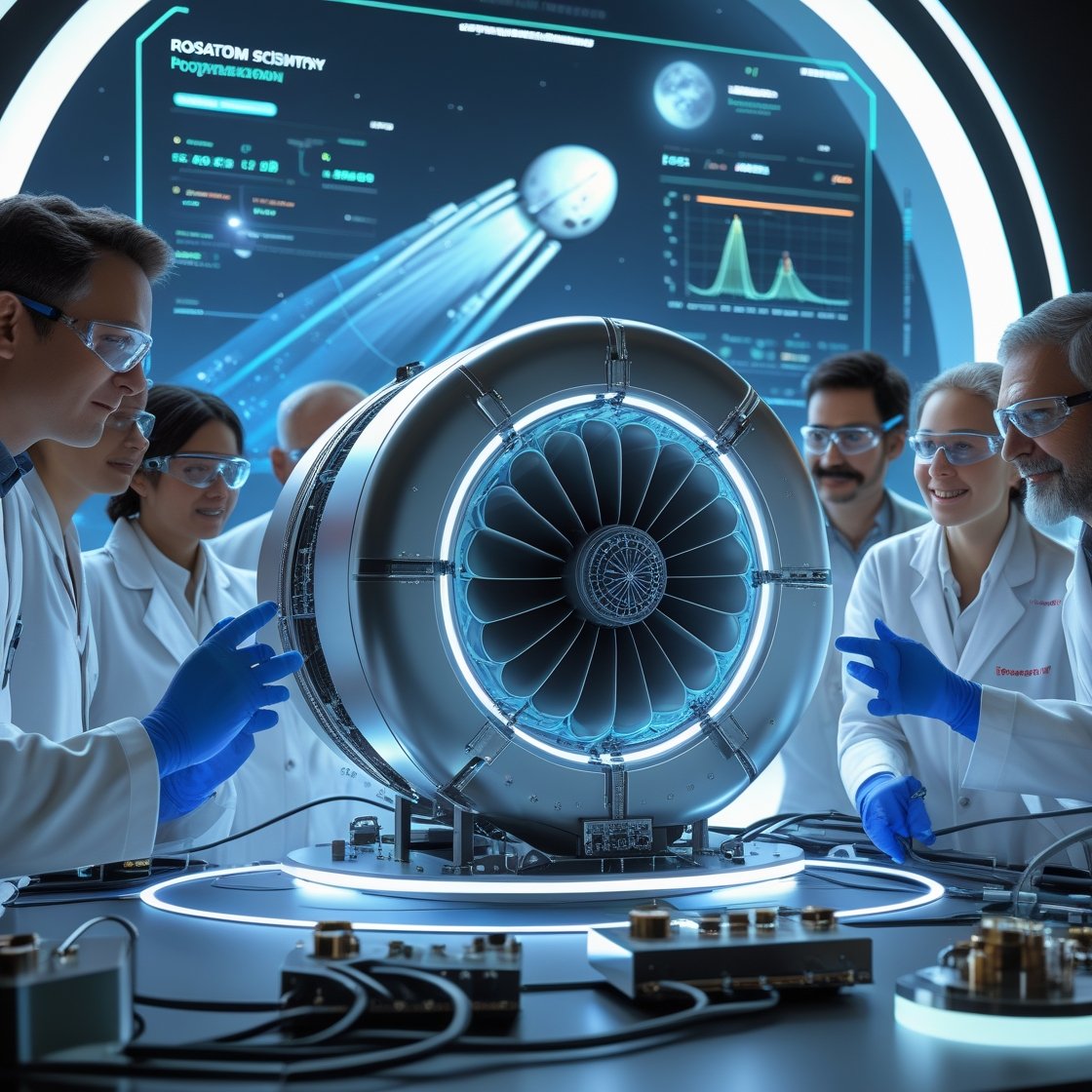

### The Plasma Rocket Engine: A New Era in Space Propulsion
For years, space agencies have been using chemical rockets to send spacecraft on missions, including trips to Mars. However, these engines are limited by their fuel efficiency and speed. The plasma rocket engine developed by Rosatom scientists, however, operates on a different principle. Rather than relying on chemical reactions to propel spacecraft, plasma rockets harness the power of ionized gases (plasma) to create thrust.
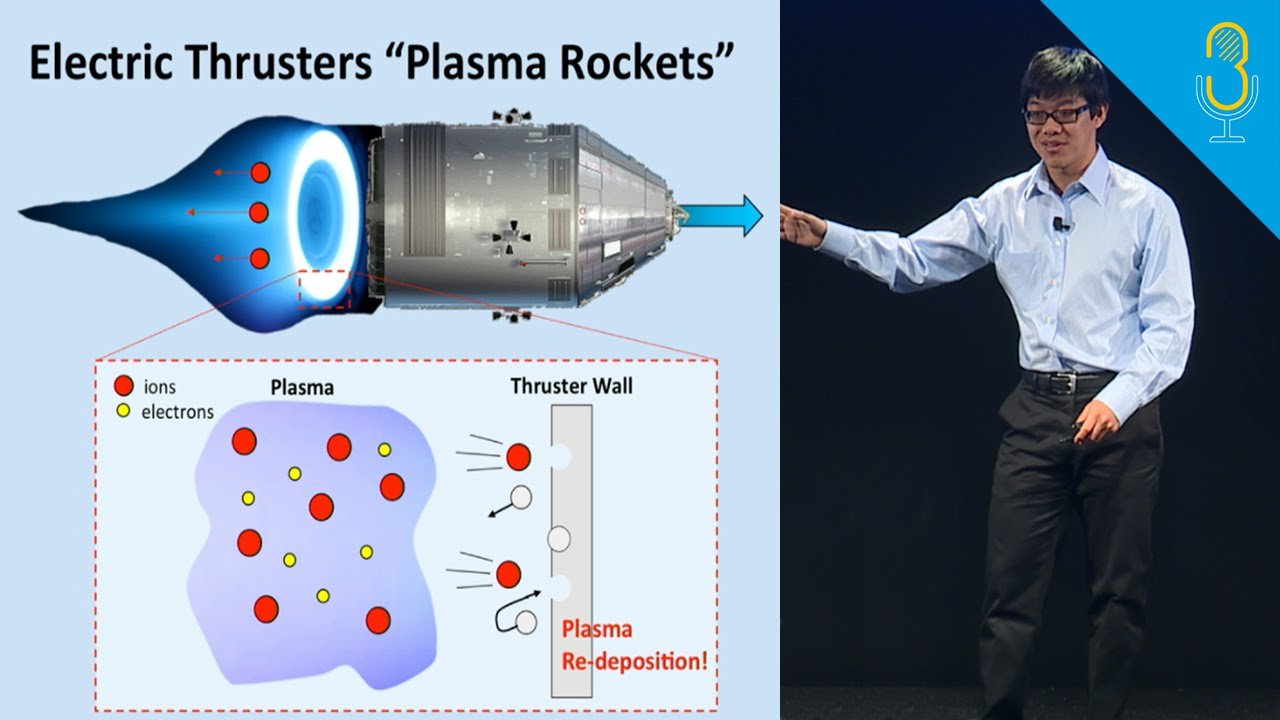
The basic mechanism involves accelerating electrically charged particles (ions) using electromagnetic fields. These ions are then expelled at high speeds, generating thrust that pushes the spacecraft forward. Unlike traditional chemical engines, plasma propulsion systems offer far greater efficiency, enabling faster travel over long distances in space. This innovation could potentially shorten what used to be a 6-9 month journey to Mars to just a few weeks.
### Mars in 30-60 Days: A Reality Within Reach
The implications of this new technology are immense. With current propulsion systems, a manned mission to Mars typically takes around 6 to 9 months, even with the most advanced rockets. The time-consuming journey presents numerous challenges, including radiation exposure, life-support systems, and psychological stress on astronauts. By significantly cutting down travel time, the plasma rocket engine opens up the possibility for more practical and sustainable missions.
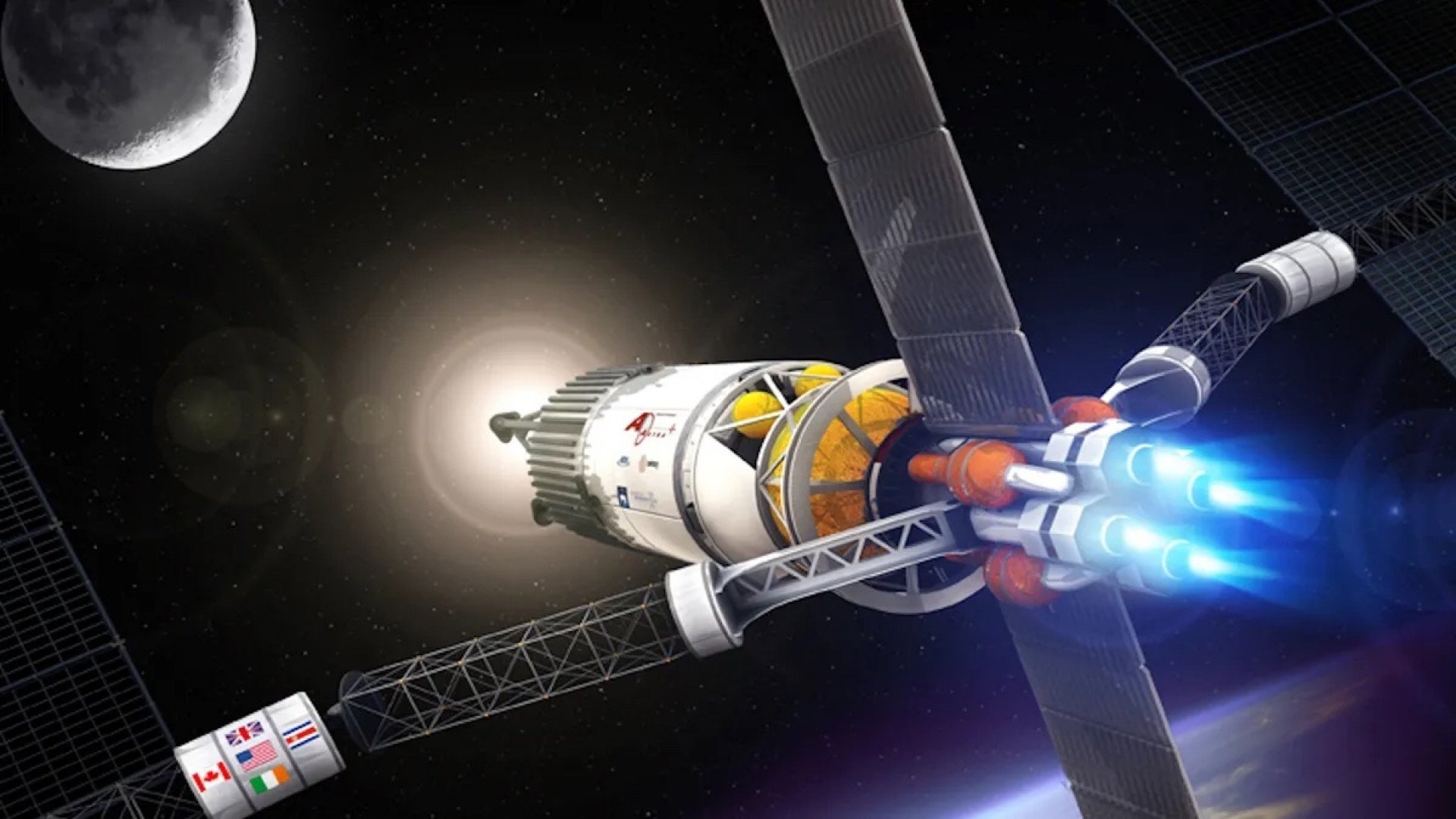

Rosatom’s prototype engine, if successfully tested and developed for use in space missions, could make it possible to reach Mars in just 30 to 60 days, drastically reducing the risks associated with long-duration space travel. This achievement would allow astronauts to spend less time in space, which could mitigate some of the health risks associated with extended exposure to microgravity and cosmic radiation. Additionally, a faster journey would enable more efficient exploration of Mars, helping scientists gather more data in less time.
### The Science Behind Plasma Propulsion
Plasma propulsion, also known as ion propulsion, has been studied for decades, but it has always faced challenges regarding efficiency and practicality for deep-space missions. Rosatom scientists, however, have made significant strides in improving the performance and reliability of these engines. The prototype engine they’ve developed is based on the principle of magnetic confinement, a technology that uses powerful magnetic fields to contain and direct the plasma in a controlled manner.
One of the most significant advantages of plasma propulsion is its fuel efficiency. Traditional chemical rockets require large amounts of fuel to generate thrust, which limits their capacity and efficiency. Plasma rockets, on the other hand, use very little fuel because they rely on electricity to accelerate ions, making them much more efficient in the long run. This means spacecraft using plasma engines could carry more payload or stay in space for longer durations without needing to refuel.
### Rosatom’s Role in Advancing Space Technology
Rosatom, Russia’s state-owned nuclear energy corporation, is known for its significant advancements in nuclear power and technology, but its involvement in space exploration is less widely known. However, the company’s investment in developing space propulsion technologies, including plasma rockets, showcases its expanding role in the space race. By using its expertise in nuclear energy and advanced engineering, Rosatom has positioned itself as a key player in the next generation of space travel.
The success of Rosatom’s plasma rocket engine also highlights the importance of international collaboration in space exploration. If this technology continues to develop at its current pace, it could significantly reduce the costs and risks associated with space missions, including those to Mars, the Moon, and beyond. With private companies like SpaceX and government agencies like NASA also working on their own advanced propulsion systems, the future of space travel is rapidly evolving.
### The Road Ahead: Testing, Development, and Potential Challenges
While the prototype engine is an exciting first step, much work remains to be done before it can be deployed for actual space missions. The next phase will involve rigorous testing, including simulations in space-like environments, to ensure the engine’s reliability and efficiency. Additionally, engineers will need to work on optimizing the system for long-duration spaceflight and ensuring that it can withstand the harsh conditions of deep space.
Challenges also remain in terms of scaling the technology for human spaceflight. Plasma engines, while efficient, still face challenges in producing enough thrust for human missions. This means further engineering innovations will be needed to develop a system that can safely carry astronauts and large payloads to Mars and other deep-space destinations.
### The Bigger Picture: Space Exploration and the Future of Humanity
Rosatom’s development of the plasma rocket engine is just the beginning of what could be a new era in space exploration. As humanity looks to extend its reach beyond Earth, faster and more efficient travel to destinations like Mars and the asteroid belt will be critical. The ability to reduce travel time from months to weeks could make it possible to establish a permanent human presence on Mars in the not-so-distant future.
Additionally, advancements in plasma propulsion could lead to missions to more distant parts of our solar system, such as the outer planets and their moons, as well as interstellar exploration. As the technology matures, it could open up new possibilities for mining asteroids, studying distant planets, and potentially even visiting exoplanets in other star systems.
### A Leap Forward for Deep-Space Missions
Rosatom’s plasma rocket engine prototype represents a revolutionary leap forward in the field of space propulsion. The ability to reach Mars in just 30 to 60 days is a game-changer, offering hope for more efficient, safer, and cost-effective missions to the Red Planet and beyond. While the technology is still in its early stages, its potential to reshape the future of space exploration is undeniable.
As we stand on the cusp of this new era, one thing is clear: the dream of interplanetary travel is no longer a distant fantasy, but a very real possibility for the future. With innovations like these, humanity’s journey into the stars may be closer than ever before.
