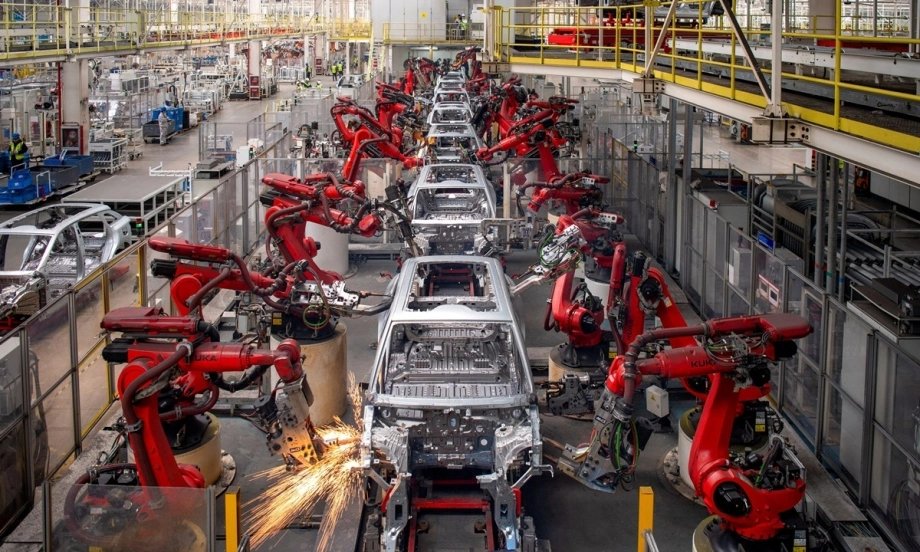
In recent years, the United States has implemented a series of tariffs targeting Chinese goods, aiming to rebalance trade relations between the two economic superpowers. These tariffs have put substantial pressure on Chinese manufacturers, pushing them to innovate and find alternative strategies to maintain their competitiveness. One of the most remarkable responses has been the rapid adoption of robot technology across various industries. By embracing automation and robotics, China has managed to cushion the impact of US tariffs, enhance productivity, and secure its position in the global supply chain.
## The Rise of Automation in Chinese Manufacturing
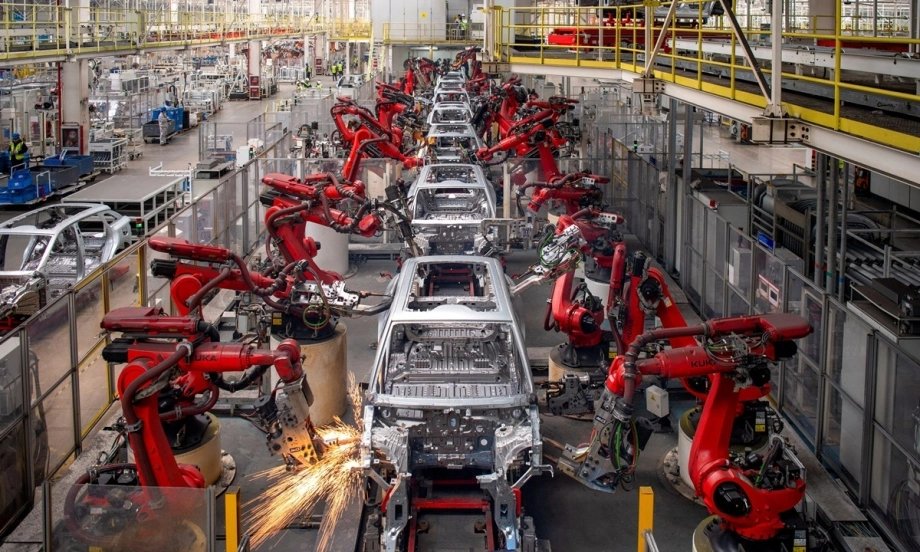

Chinese manufacturers, particularly in sectors like electronics, textiles, and machinery, have faced rising production costs due to tariffs. To mitigate these challenges, companies have increasingly turned to robotics and automation. Industrial robots are now performing tasks that were once labor-intensive, including assembly, welding, painting, and packaging.
By integrating robots into their production lines, Chinese firms have significantly improved efficiency, reduced reliance on manual labor, and maintained stable production levels even in the face of trade disruptions. This shift has been essential in ensuring that China remains a manufacturing powerhouse despite the external economic pressures.
## Government Support for Robotic Innovation
The Chinese government has played a crucial role in promoting the adoption of robot technology. Initiatives like the “Made in China 2025” plan have emphasized the importance of upgrading the country’s manufacturing base with advanced technologies, including robotics and artificial intelligence (AI).
Subsidies, tax incentives, and research grants have encouraged companies to invest in automation. Moreover, local governments have established “robot towns” and innovation hubs designed to support robotics startups and foster technological collaboration. This comprehensive policy support has accelerated the integration of robots into the Chinese industrial ecosystem, strengthening the nation’s resilience against external economic shocks like US tariffs.
## Robots Reduce Labor Costs and Increase Efficiency
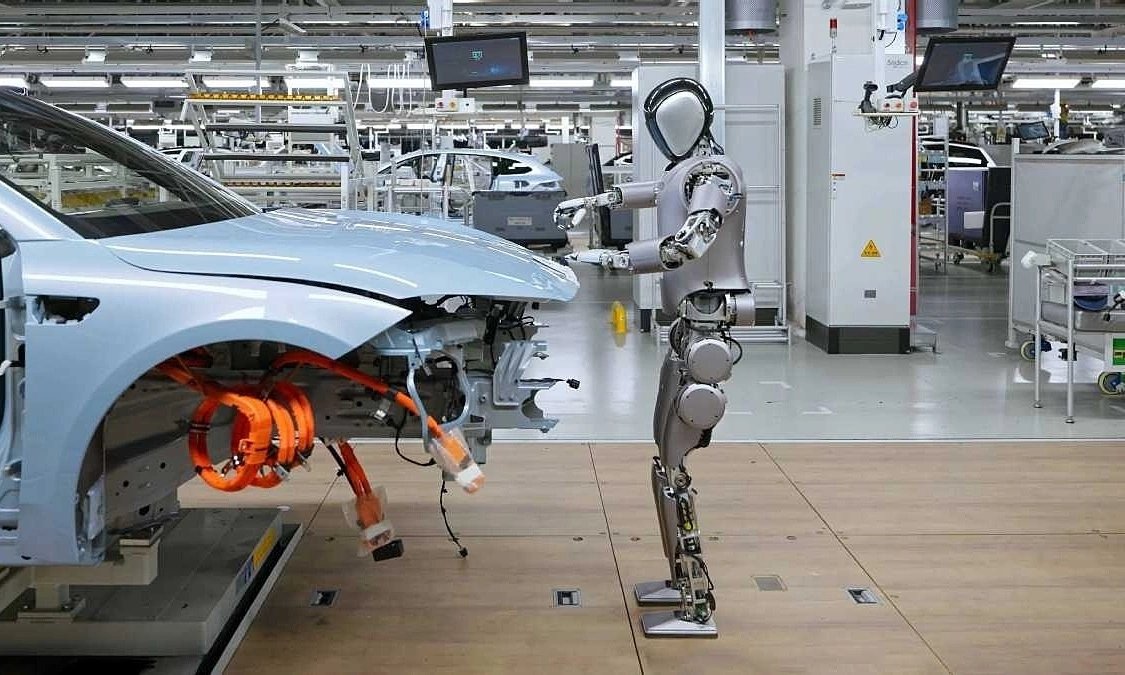

One of the immediate benefits of robot technology is the reduction in labor costs. As wages in China have gradually increased over the years, robots provide a more cost-effective solution for tasks that require speed, precision, and consistency.
Unlike human workers, robots can operate around the clock without breaks, vacations, or shifts. This 24/7 operational capability dramatically boosts productivity, enabling companies to meet international demand even with higher export costs caused by tariffs. Furthermore, the precision and quality control offered by robots have helped Chinese manufacturers deliver products that meet stringent international standards, thus preserving their market share.
## Impact on Different Sectors
### Electronics and Consumer Goods
The electronics industry has been at the forefront of robotic integration. Companies manufacturing smartphones, laptops, and other gadgets have automated delicate processes like soldering tiny components onto circuit boards. Robotics ensures higher accuracy and speed, leading to faster turnaround times and lower defect rates.
### Textile and Apparel
In the traditionally labor-intensive textile sector, robots are being deployed for tasks like fabric cutting, sewing, and dyeing. Automation reduces the dependency on a large workforce and helps companies maintain competitiveness despite tariffs that would otherwise erode profit margins.
### Automotive Industry
China’s automotive industry has also benefited enormously from robotics. Robots perform welding, painting, and assembly with superior precision, resulting in higher-quality vehicles produced at lower costs. This efficiency has allowed Chinese car manufacturers to explore new markets and expand their global footprint, offsetting losses caused by reduced US market access.
## Technological Advancements Driving the Revolution
Several technological breakthroughs have fueled the surge in robot adoption:
– **Artificial Intelligence**: AI-enabled robots can learn from their environment and optimize their tasks over time, improving their efficiency without human intervention.
– **Machine Vision**: Robots equipped with advanced vision systems can perform intricate quality inspections, identifying defects invisible to the human eye.
– **Collaborative Robots (Cobots)**: Unlike traditional industrial robots confined to cages, cobots work alongside human workers, enhancing flexibility on the production floor.
– **5G Connectivity**: High-speed wireless communication allows robots to operate in smart factories, exchanging real-time data to optimize workflows.
These innovations have not only improved the capabilities of robots but also made them more affordable and accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), democratizing automation across China.
## Challenges and Adjustments
While the adoption of robot technology has yielded numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges. The upfront investment for automation is substantial, and not all companies can afford it immediately. There is also a learning curve associated with integrating robots into existing workflows.
Furthermore, the transition to automation has significant implications for employment. Traditional manufacturing jobs are declining, creating a need for workforce retraining programs to help workers adapt to new roles, such as robot maintenance, programming, and system management. The Chinese government and private sector are actively investing in vocational training and educational initiatives to bridge this skills gap.
## Strengthening Supply Chain Resilience
Robot technology has not only helped China maintain production levels but also enhanced supply chain resilience. Automated factories are less vulnerable to labor shortages, pandemics, or political disruptions.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many Chinese factories equipped with robots were able to continue operations with minimal staff, meeting global demand for essential goods like medical equipment and electronics. This resilience has strengthened China’s reputation as a reliable supplier, even in turbulent times.
## Expanding Beyond Domestic Markets

With tariffs making exports to the US more expensive, Chinese companies have diversified their markets. Automation allows them to produce high-quality goods efficiently, making them more competitive in emerging markets such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
By leveraging robotics, Chinese firms are not just surviving but thriving in new regions, building global brands, and reducing their dependence on any single market, including the US.
## Robotics Industry: A New Pillar of Economic Growth
The demand for industrial robots has created a booming robotics industry within China. Domestic robot manufacturers like Siasun, Estun, and Efort are growing rapidly, challenging established players from Japan, Germany, and the US.
China is no longer just a user of robotic technology; it is becoming a global leader in robotics innovation, developing cutting-edge solutions tailored for various industries. This emerging sector promises to be a vital pillar of China’s future economic growth, generating high-value jobs and advancing technological self-sufficiency.
## Case Studies: Success Stories
### Foxconn’s Robotic Transformation
Foxconn, the world’s largest electronics contract manufacturer, has famously embraced automation to cope with rising costs and tariffs. Known for assembling products like the iPhone, Foxconn has deployed over 100,000 robots across its factories, aiming for a future where fully automated production lines become the norm.
### Textile Automation in Zhejiang Province
In Zhejiang Province, numerous textile companies have replaced traditional sewing lines with robotic systems capable of producing garments at incredible speed and precision. These companies have maintained competitiveness in the global market, even as export conditions have grown tougher due to US tariffs.
## Future Outlook: Robotics and China’s Industrial Evolution

Looking ahead, China’s commitment to robot technology is expected to deepen. Advances in AI, quantum computing, and materials science will lead to even smarter, more capable robots.
Smart factories — where robots, AI systems, and big data analytics converge — will become increasingly common. China’s focus on self-reliance, innovation, and industrial upgrading suggests that robot technology will remain at the core of its strategy to withstand external economic pressures and drive long-term growth.
## Conclusion: Innovation as a Shield Against Adversity
The imposition of US tariffs on Chinese goods could have been a devastating blow to China’s manufacturing sector. However, through a strategic embrace of robot technology, China has turned adversity into an opportunity for transformation.
Automation has not only allowed Chinese companies to maintain production and competitiveness but has also paved the way for a new era of technological leadership. As robot technology continues to evolve, China is well-positioned to adapt to future challenges and reinforce its status as a global economic powerhouse.
By investing in robotics and fostering a culture of innovation, China has demonstrated that technological advancement can be a powerful shield against external economic pressures — and a catalyst for a more resilient and prosperous future.
