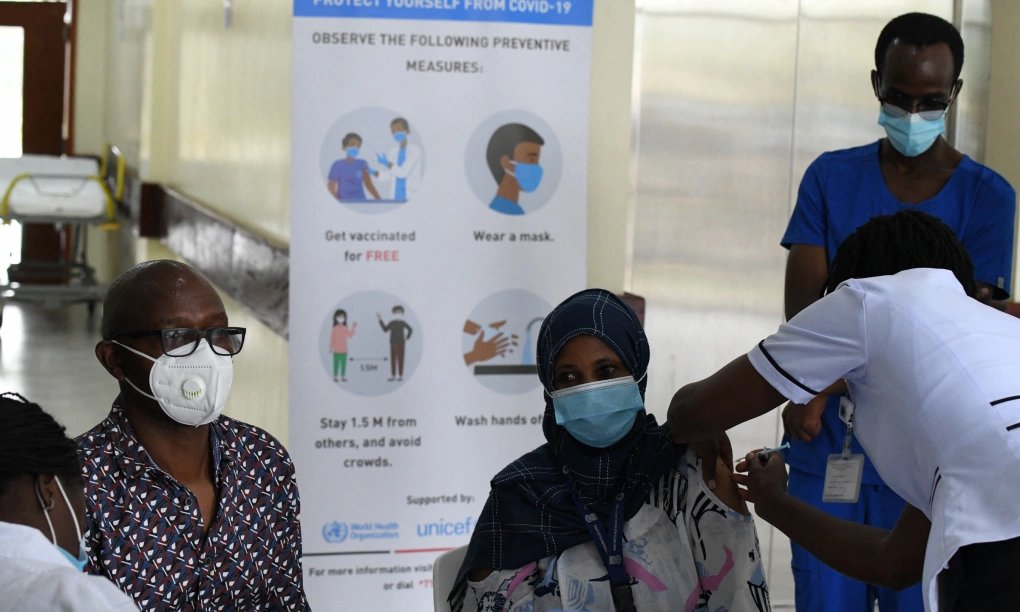
The United States has been a key player in global public health initiatives, particularly in supporting vaccination programs for developing countries. However, recent reports indicate that the U.S. government may halt or significantly reduce its funding for these programs. This decision has sparked concerns among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and humanitarian organizations worldwide. If the U.S. withdraws its support, the consequences could be dire, particularly for low-income nations that rely on American aid to combat infectious diseases. This article explores the potential reasons behind this move, its implications, and possible alternatives to mitigate the impact.
## The Role of the U.S. in Global Vaccine Programs
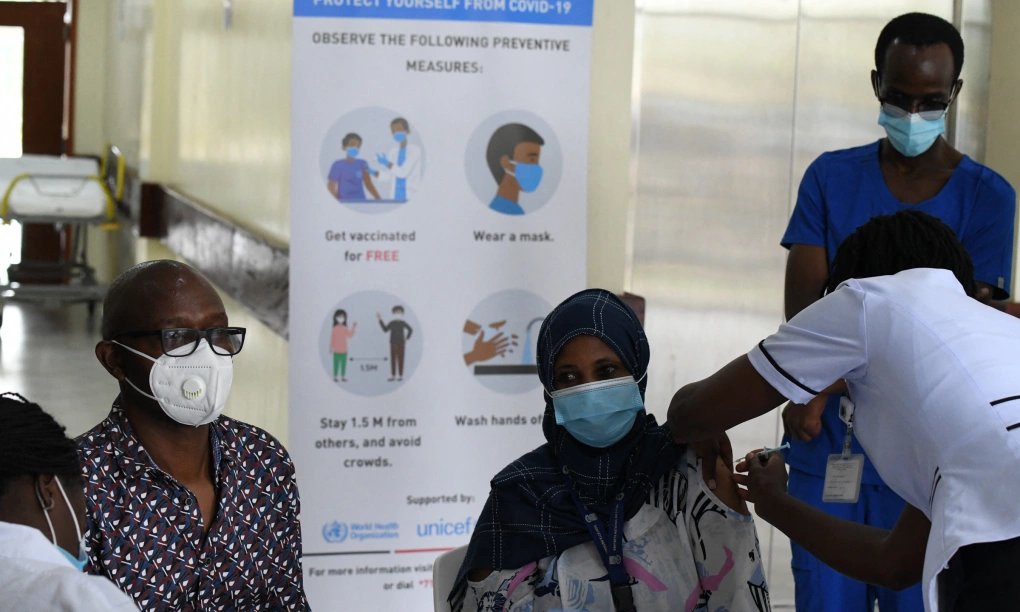
For decades, the U.S. has played a crucial role in supporting global vaccination efforts. Programs like Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, and COVAX have benefited immensely from U.S. contributions. Through financial aid, logistical support, and research funding, the country has helped immunize millions of children and adults against deadly diseases such as measles, polio, and COVID-19. These efforts have significantly reduced mortality rates and improved overall global health security.
### Key Contributions of the U.S. to Global Vaccination Efforts
– **Financial Support**: The U.S. has been one of the largest donors to international vaccine programs, contributing billions of dollars annually.
– **Research and Development**: American pharmaceutical companies and research institutions have been at the forefront of developing life-saving vaccines.
– **Logistical Aid**: U.S. agencies, including USAID and the CDC, have played a critical role in distributing vaccines to remote areas.
## Why the U.S. May Stop Supporting Vaccine Programs
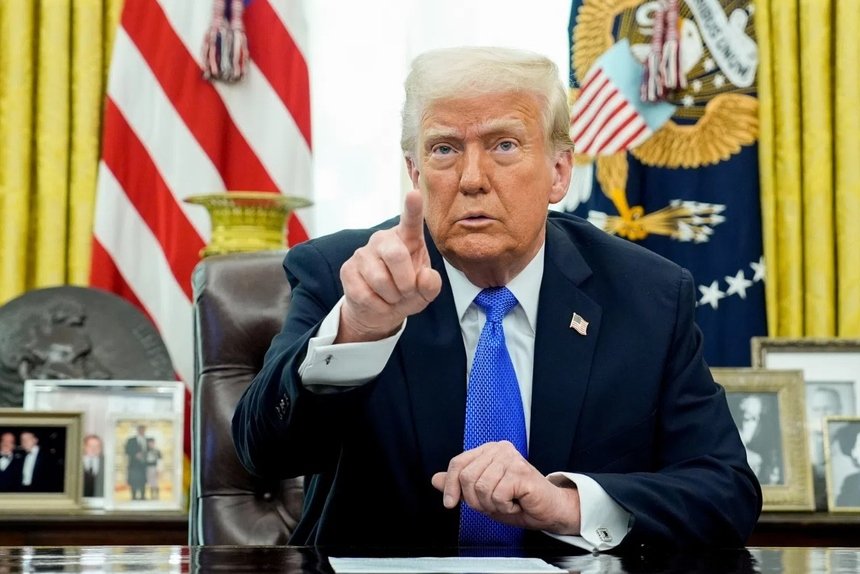

Several factors might be driving the U.S. government’s reconsideration of its financial support for global vaccine programs:
### 1. **Economic Constraints**
The U.S. economy has faced significant challenges in recent years, including inflation, rising national debt, and budget deficits. As a result, the government may prioritize domestic spending over foreign aid, including vaccine programs.
### 2. **Political Shifts**
Changes in administration and political ideologies can influence foreign aid policies. Some policymakers argue that funds should be redirected to domestic health initiatives rather than international programs.
### 3. **Pandemic Fatigue**
The COVID-19 pandemic prompted unprecedented spending on global health initiatives. As the crisis subsides, there may be reduced urgency to continue funding vaccine programs abroad.
### 4. **Geopolitical Considerations**
The U.S. has been recalibrating its foreign policy, focusing more on economic competition with China and Russia. This shift may lead to reduced funding for non-strategic humanitarian efforts.
## Potential Consequences of U.S. Withdrawal from Vaccine Support

If the U.S. ceases to fund global vaccine initiatives, the impact could be severe, particularly in developing countries. Some of the potential consequences include:
### 1. **Increased Disease Outbreaks**
Many developing countries lack the infrastructure to produce and distribute vaccines independently. A funding cut could lead to a resurgence of preventable diseases, endangering millions of lives.
### 2. **Higher Child Mortality Rates**
Vaccines have played a crucial role in reducing infant and child mortality rates worldwide. Without continued support, many children may lose access to life-saving immunizations.
### 3. **Global Economic Consequences**
Health crises in developing nations can have widespread economic repercussions. Disease outbreaks can disrupt trade, reduce productivity, and strain healthcare systems globally.
### 4. **Loss of U.S. Global Influence**
By withdrawing from vaccine support, the U.S. risks losing its position as a global health leader. This vacuum could be filled by other nations, particularly China, which has been expanding its influence in global health initiatives.
## Possible Alternatives and Solutions

Despite the challenges, alternative strategies can help mitigate the impact of reduced U.S. funding for vaccine programs.
### 1. **Encouraging Private Sector Involvement**
Pharmaceutical companies, philanthropic organizations, and tech giants can play a more significant role in funding and distributing vaccines. Initiatives like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation have already demonstrated the effectiveness of private sector involvement in global health.
### 2. **Strengthening International Partnerships**
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Union, and other wealthy nations can step in to fill the funding gap left by the U.S.
### 3. **Developing Local Vaccine Manufacturing**
Investing in vaccine production facilities in developing countries can reduce reliance on foreign aid. Countries like India and Brazil have already made significant strides in this area.
### 4. **Advocacy and Public Pressure**
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and advocacy groups can play a crucial role in lobbying for continued U.S. support for global vaccine initiatives. Public pressure can influence policymakers to reconsider funding cuts.
## Conclusion
The potential decision of the U.S. to stop supporting vaccines for developing countries could have far-reaching consequences. Increased disease outbreaks, higher child mortality rates, economic disruptions, and a decline in U.S. global influence are all possible outcomes. However, through international cooperation, private sector involvement, and innovative solutions, the global community can work together to ensure that vulnerable populations continue to receive the vaccines they need. As the world moves forward, it is crucial for governments, organizations, and individuals to recognize the importance of sustained investment in global health security.